Public Docs
【模型量化】深度学习模型量化 & 量化理论 & 各平台的量化过程 & 硬件加速
【TVM】TI关于TVM的使用测试与分析
【LLM&LVM】大模型开源工程思维导图
SmartSip
【北航卓越工程师】《汽车前沿技术导论:智能驾驶》讲义
【工具链】Yocto使用介绍——使用Yocto创建一个树莓派的系统镜像
【工具链】使用ssh+dialog指令设定服务器指定用户仅容器访问
【推理引擎】一篇关于模型推理的详细对比与学习
【推理引擎】关于TVM中的Schedule优化详解(On going)
【LLM微调】使用litgpt进行私有数据集模型微调的测试总结
【TVM】在TVM Relay中创建一个自定义操作符
【STT+LLM+TTS】如何使用语音转文字模型+大预言模型+语音生成模型完成一个类人的语音交互机器人
【RAG】 通过RAG构建垂直领域的LLM Agent的方法探索
【RAG】GraphRAG精读与测试(On going)
【AI Agent】MetaGPT精读与学习
【AI Base】Ilya Sutskever 27篇必读论文分享清单
【Nvidia】Jetson AGX Orin/ Jetson Orin nano 硬件测试调试内容(On going)
【BI/DI】LLM Using in BI Testing Scenario (On going)
【Nvidia】How to Activate a Camera on Nvidia Platform in Details
【RAS-PI】树莓派驱动开发
【行业咨询阅读】关注实时咨询和分析
【mobileye】2024 Driving AI
【mobileye】SDS_Safety_Architecture
【yolo】yolov8测试
【nvidia】Triton server实践
【alibaba】MNN(on updating)
【OpenAI】Triton(on updating)
【CAIS】关于Compound AI Systems的思考
【Nvidia】关于Cuda+Cudnn+TensorRT推理环境
【BEV】BEVDet在各个平台上的执行效率及优化(On Updating)
【Chip】AI在芯片设计和电路设计中的应用
【Chip】ChiPFormer
【Chip】关于布线的学习
【Chip】MaskPlace论文精读与工程复现优化
【gynasium】强化学习初体验
【Cadence】X AI
【transformer】MinGPT开源工程学习
【中间件】针对apollo 10.0中关于cyberRT性能优化的深度解读和思考
【Robotics】调研了解当前机器人开发者套件(on updating)
【Robotics】ROS CON China 2024 文档技术整理与感想总结(上2024.12.7,中2024.12.8,下场外产品)
【algorithm】关于模型、数据与标注规范的平衡问题
【nvidia】DLA的学习了解与使用
【nvidia】构建nvidia嵌入式平台的交叉编译环境(其他环境平台可借鉴)
【2025AI生成式大会】2025大会个人总结
【Robotics】 Create Quadruped Robot RL FootStep Training Environment In IsaacLab
【Robotics】如何一个人较为完整的完成一个机器人系统软件算法层面的设计与开发
【VLM】读懂多模态大模型评价指标
【VLM】大模型部署的端侧部署性能与精度评估方法与分析
【Nvidia】Jetson Orin 平台VLM部署方法与指标评测
【Database】向量数据库
【SoC】性能与功耗评估
【MCP】MCP探索
文档发布于【Feng's Docs】
-
+
首页
【推理引擎】一篇关于模型推理的详细对比与学习
# 一篇关于模型推理的详细对比与学习 ## 1.Intro 通过一直对模型推理和计算加速的兴趣,这些年测试过了许多模型推理相关的框架和技术。有一些`专有平台`的如TI的TIDL/TIDLRT,有NXP平台的APEX,NVIDIA的TensorRT。除了在端上的还有例如寒武纪,华为晟腾这样的云计算数据中心芯片提供商的云加速推理方案。这些适用于专有平台的推理框架(或叫工具包),基于对芯片架构的了解,能够极大程度的针对特定算子做出性能极高的优化。 但是,这些专有平台的缺点也极为明显,由于没有大规模的测试和适配过一些日新月异的算子搭配和变革,在有些时候也会表现出一些功能或者性能的异常。由于本身的黑盒特性,当用户发现诸如此类的问题时,如果没有开发人员或FAE的协助,很难有效的解决相关问题。 所以一些`纯开放或者半开放的框架`诸如TVM,NCNN,ONNXruntime等也一定程度上丰富和拓展了用户的选择,使得一些资深人员可以基于一个纯白盒的方式去拓展。 抱着对这些技术强烈的好奇,我在学习TVM的过程中,==想平行对比一下在同一个网络上这些普通推理框架的性能,同时也想测试一下针对自定义算子的开发易用性==。这将是一篇长学习文档。我将逐步更新我的学习过程。 * 先展示下测试结果,再详细看之后的测试过程: 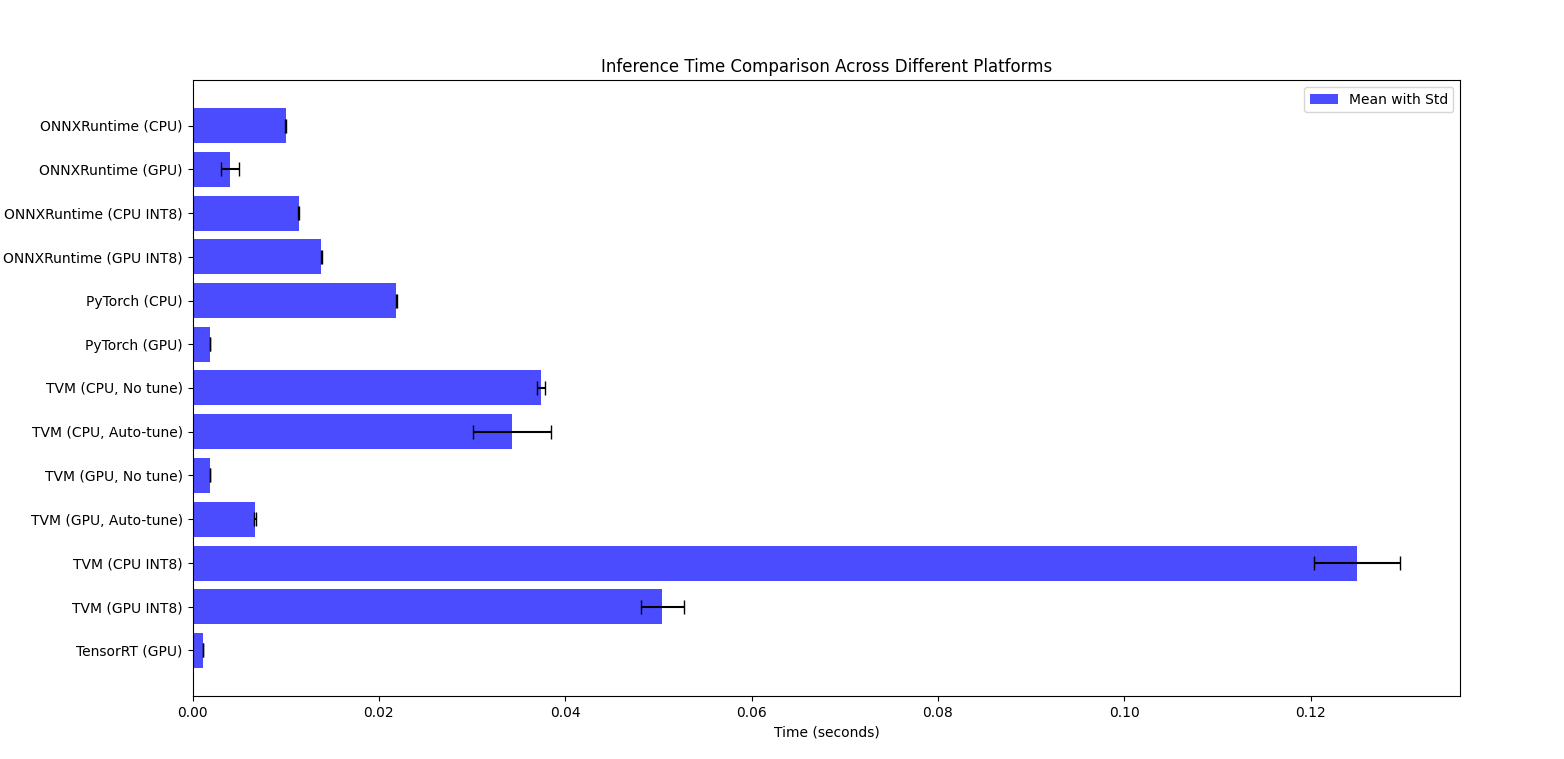 * Life of IRModule in TensorIR ``` mermaid graph TD; A[TVM Script - based python-AST allow program, write complex programs] -- Parse --> B[IRModule]; C[Tensor Expression - TE DSL, schedule, optimize] -- Convert --> B; B -- Print --> A; B -- schedule Transform --> B; B -- Pass Transform --> B; B -- Build --> D[Runnable Module]; B -- Transform --> E[Relay]; E -- Display --> F[RelayIR - Relay IR 以函数的形式定义是 TVM 的中间表示, 用于定义, 优化和编译深度学习模型]; E -- Save --> G[JSON-Serialization - JSON 序列化形式是将 Relay IR 模型转换为一种便于保存和传输的格式. ]; ``` * TensorIR interactive optimization flow 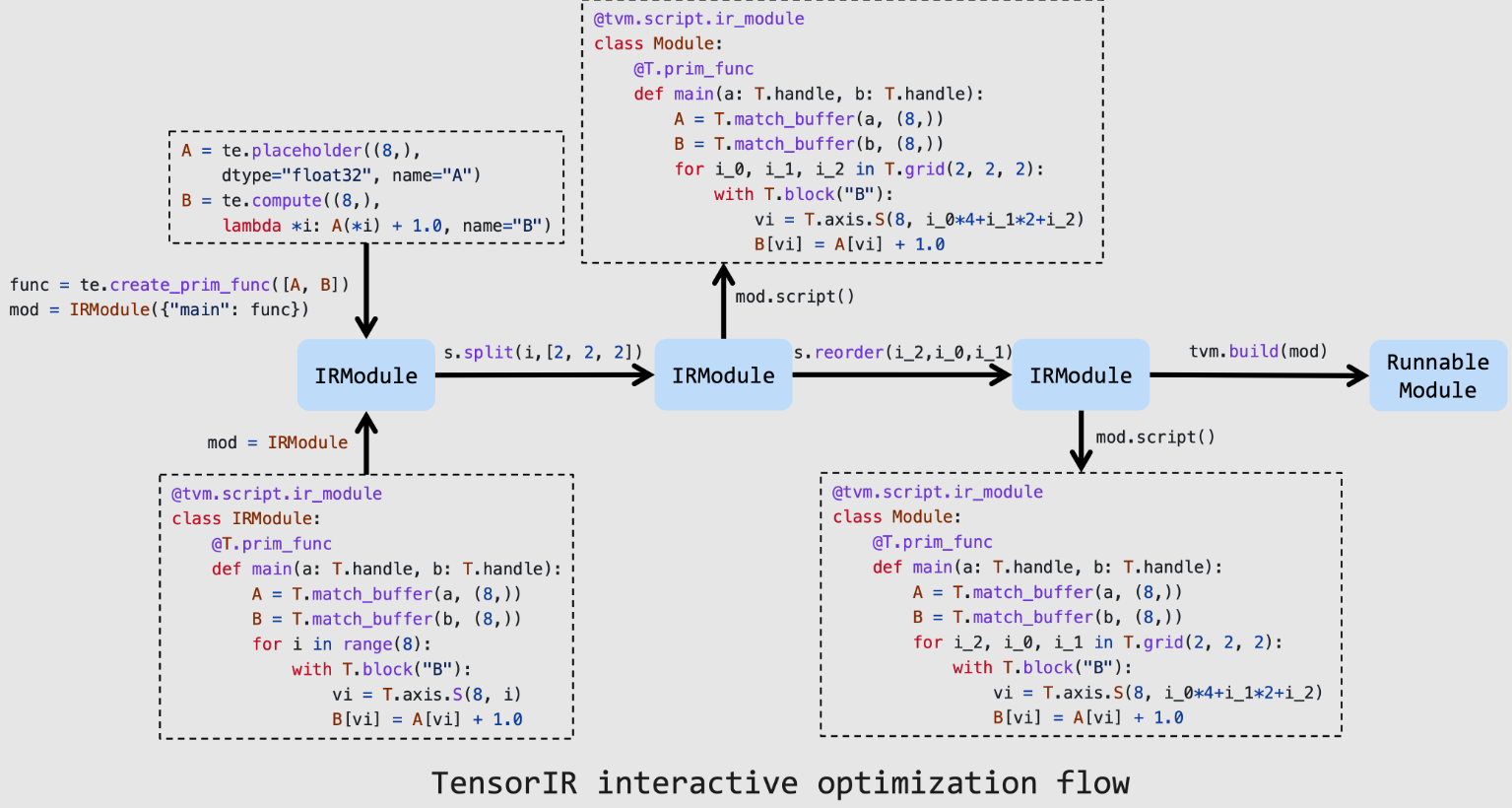 ## 2.Pre-acknowledges from Internet about the different inference framework 1. TensorRT Performance: TensorRT is highly optimized for NVIDIA GPUs and typically offers the best performance in terms of latency and throughput. It takes advantage of low-level GPU optimizations, including precision calibration (FP16, INT8), kernel fusion, and layer optimization. Ease of Use: Requires model conversion from frameworks like PyTorch to ONNX and then to TensorRT. Some additional tuning and calibration might be needed for optimal performance. 2. ONNX Runtime Performance: ONNX Runtime provides good performance, especially when using the GPU execution provider. While it might not match TensorRT's performance, it is quite efficient and easier to integrate with models already exported to ONNX. Ease of Use: Straightforward if you have an ONNX model. It supports various optimizations and execution providers, including NVIDIA GPUs. 3. TVM Performance: TVM can offer excellent performance by compiling models specifically optimized for the target hardware. Performance can be close to or even surpass TensorRT in some cases, depending on the level of optimization and tuning. Ease of Use: Requires more effort to tune and optimize. The process involves compiling the model specifically for the hardware, which can be complex and time-consuming. 4. PyTorch Performance: PyTorch is generally not as optimized for inference on GPUs compared to the other specialized inference engines. Performance can be improved with TorchScript and using the PyTorch native AMP (Automatic Mixed Precision) for FP16 operations. Ease of Use: Easiest to use if the model is already in PyTorch. Minimal code changes are needed to run the model in inference mode. Performance Comparison Summary `TensorRT`: Typically offers the best performance on NVIDIA GPUs, especially with FP16/INT8 optimizations. `ONNX Runtime`: Good performance and easier integration if you have an ONNX model. `TVM`: Potentially very high performance but requires significant tuning and expertise. `PyTorch`: Good for ease of use but generally not as fast as the others for GPU inference. ## 3. The Tests ### 3.1. Utils `Model`: https://github.com/onnx/models/raw/b9a54e89508f101a1611cd64f4ef56b9cb62c7cf/vision/classification/resnet/model/resnet50-v2-7.onnx (we use a Resnet50v2 model,the input is 1 * 3 * 224 * 224,the output is 1 * 1000) [【附件】resnet50-v2-7.onnx.png](/media/attachment/2024/05/resnet50-v2-7.onnx.png) `Input Data`: https://s3.amazonaws.com/model-server/inputs/kitten.jpg (224 * 224 * 3(rgb)) [【附件】kitten (1).jpg](/media/attachment/2024/05/kitten_1.jpg) `Label`: https://s3.amazonaws.com/onnx-model-zoo/synset.txt (class 1000) ### 3.2. OnnxRuntime #### 3.2.1. Float32(GPU, CPU) ``` python import onnxruntime as ort import numpy as np import time import timeit from PIL import Image # https://github.com/onnx/models/raw/b9a54e89508f101a1611cd64f4ef56b9cb62c7cf/vision/classification/resnet/model/resnet50-v2-7.onnx model_path = "resnet50-v2-7.onnx" # https://s3.amazonaws.com/model-server/inputs/kitten.jpg img_path = 'kitten.jpg' # Resize it to 224x224 resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224)) img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32") # Our input image is in HWC layout while ONNX expects CHW input, so convert the array img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1)) # Normalize according to the ImageNet input specification imagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) norm_img_data = (img_data / 255 - imagenet_mean) / imagenet_stddev # Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW. input_data = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0).astype("float32") # timing_number should be bigger, if it is 10, no difference between cpu and gpu timing_number = 200 timing_repeat = 10 # cpu execute time def run_model_cpu(model_path, input_data): session_cpu = ort.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']) print("Available cpu providers: ", session_cpu.get_providers()) input_name = session_cpu.get_inputs()[0].name cpu_result = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: session_cpu.run(None, {input_name: input_data})).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) cpu_result = {"mean": np.mean(cpu_result), "median": np.median(cpu_result), "std": np.std(cpu_result)} print("Onnxruntime_CPU_Float32: %s" % (cpu_result)) # gpu execute time def run_model_gpu(model_path, input_data): try: session_gpu = ort.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider']) print("Available GPU providers: ", session_gpu.get_providers()) except Exception as e: print("Error initializing GPU session: ", e) return input_name = session_gpu.get_inputs()[0].name gpu_result = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: session_gpu.run(None, {input_name: input_data})).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) gpu_result = {"mean": np.mean(gpu_result), "median": np.median(gpu_result), "std": np.std(gpu_result)} print("Onnxruntime_GPU_Float32: %s" % (gpu_result)) run_model_cpu(model_path, input_data) run_model_gpu(model_path, input_data) ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash # CPU class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621104 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356378 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 # GPU class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621105 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356377 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019713 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 Available cpu providers: ['CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_CPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.009986212425981647, 'median': 0.009982698982494185, 'std': 1.576711878851109e-05} Available GPU providers: ['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_GPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.004069052441569511, 'median': 0.0037474105950968803, 'std': 0.0009607391846988234} ``` #### 3.2.2. Int8(GPU, CPU) After thorough performance analysis, we've observed that on CPUs, the application of INT8 quantization indeed yields significant performance improvements. This technique accelerates processing speed by reducing the data width required during model computations, all while maintaining the model's accuracy. Considering that the ResNet50 model is relatively small compared to other models, its performance on CPUs and GPUs exhibits no significant difference. This consistency in efficiency provides us with flexibility, allowing us to seamlessly switch between different hardware configurations without the concern of performance loss. Further experiments have corroborated this finding. When testing the ResNet152 model with similar benchmarks, we also observed no discernible difference in inference speed between CPUs and GPUs. This suggests that for models of this size, the choice of hardware platform depends more on available resources and specific application scenarios rather than sheer performance considerations.  * Model Quant(Onnx Model Quant is only Available for int8) ``` python from onnxruntime.quantization import quantize_dynamic, QuantType help(QuantType) ```  * Quant the model from float32 to int8 ```python import onnx import onnxruntime as ort import numpy as np import timeit from onnxruntime.quantization import quantize_dynamic, QuantType # Define paths model_fp32 = "resnet50-v2-7.onnx" model_int8 = "resnet50-v2-7-int8.onnx" img_path = 'kitten.jpg' # Load and update the model to opset 11 model = onnx.load(model_fp32) model_opset_version = model.opset_import[0].version if model_opset_version < 11: print(f"The original model opset version is {model_opset_version}, updating to opset 11.") model = onnx.version_converter.convert_version(model, 11) onnx.save(model, "resnet50-v2-11.onnx") model_fp32 = "resnet50-v2-11.onnx" # Quantize the model quantized_model = quantize_dynamic(model_fp32, model_int8, weight_type=QuantType.QUInt8) print(f"Quantized model saved to {model_int8}") ``` * Just Load the int8 model ``` python model_path = "resnet50-v2-7-int8.onnx" ``` * Execution Result: ```bash # CPU Resnet50 class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.657020 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.316742 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.023232 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001320 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000253 # GPU Resnet50 class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.647389 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.325191 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.024315 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001383 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000234 # CPU Resnet152 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.618835 class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.089756 class='n04589890 window screen' with probability=0.055205 class='n04590129 window shade' with probability=0.054228 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.041171 # GPU Resnet152 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.616358 class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.091070 class='n04589890 window screen' with probability=0.055855 class='n04590129 window shade' with probability=0.054603 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.042334 Available cpu providers: ['CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_CPU_Int8: {'mean': 0.011375669833010759, 'median': 0.011376627020072192, 'std': 1.180472312469979e-05} Available GPU providers: ['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_GPU_Int8: {'mean': 0.013842492688942002, 'median': 0.013839954254799523, 'std': 2.1459357287547657e-05} Available cpu providers: ['CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_CPU_ResNet152_Int8: {'mean': 0.03108119218947832, 'median': 0.031068197362474168, 'std': 3.971259752378018e-05} Available GPU providers: ['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'] Onnxruntime_GPU_ResNet152_Int8: {'mean': 0.03715013448652462, 'median': 0.03713770236005075, 'std': 3.551800251648068e-05} ``` ### 3.3. Pytorch #### 3.3.1. Float32(GPU, CPU) ``` python import numpy as np import timeit import torch from torchvision import models, transforms from PIL import Image img_path = 'kitten.jpg' resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224)) preprocess = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]), ]) input_tensor = preprocess(resized_image) input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True) model.eval() timing_number = 200 timing_repeat = 10 def run_model_cpu(model, input_batch): model.to('cpu') with torch.no_grad(): cpu_result = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: model(input_batch)).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) cpu_result = {"mean": np.mean(cpu_result), "median": np.median(cpu_result), "std": np.std(cpu_result)} print("Torch_CPU_Float32: %s" % (cpu_result)) def run_model_gpu(model, input_batch): if torch.cuda.is_available(): model.to('cuda') input_batch_gpu = input_batch.to('cuda') with torch.no_grad(): gpu_result = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: model(input_batch_gpu)).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) gpu_result = {"mean": np.mean(gpu_result), "median": np.median(gpu_result), "std": np.std(gpu_result)} print("Torch_GPU_Float32: %s" % (gpu_result)) else: print("CUDA Invalid!") run_model_cpu(model, input_batch) run_model_gpu(model, input_batch) ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash # CPU class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.476912 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.465774 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.046519 class='n03958227 plastic bag' with probability=0.002096 class='n02971356 carton' with probability=0.000678 # GPU class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.476538 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.466136 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.046531 class='n03958227 plastic bag' with probability=0.002095 class='n02971356 carton' with probability=0.000678 Torch_CPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.021870234759990125, 'median': 0.021858943702391116, 'std': 3.487536414872911e-05} Torch_GPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.0018875277980696411, 'median': 0.0018826104051549919, 'std': 2.818227506480741e-05} ``` ### 3.4. TVM #### 3.4.1. Float32 (cpu, cpu-auto-tune) * float32 ``` python import onnx from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata from PIL import Image import numpy as np import tvm.relay as relay import tvm from tvm.contrib import graph_executor onnx_model = onnx.load('resnet50-v2-7.onnx') img_path = 'kitten.jpg' # Resize it to 224x224 resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224)) img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32") # Our input image is in HWC layout while ONNX expects CHW input, so convert the array img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1)) # Normalize according to the ImageNet input specification imagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) norm_img_data = (img_data / 255 - imagenet_mean) / imagenet_stddev # Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW. img_data = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0).astype("float32") print(img_data.shape) print(img_data.dtype) # The input name may vary across model types. You can use a tool # like Netron to check input names input_name = "data" target = "llvm" shape_dict = {input_name: img_data.shape} mod, params = relay.frontend.from_onnx(onnx_model, shape_dict) with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3): lib = relay.build(mod, target=target, params=params) dev = tvm.device(str(target), 0) module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev)) dtype = "float32" module.set_input(input_name, img_data) module.run() output_shape = (1, 1000) tvm_output = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(output_shape)).numpy() from scipy.special import softmax labels_path = "synset.txt" with open(labels_path, "r") as f: labels = [l.rstrip() for l in f] # Open the output and read the output tensor scores = softmax(tvm_output) scores = np.squeeze(scores) ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] for rank in ranks[0:5]: print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank])) import timeit timing_number = 10 timing_repeat = 10 unoptimized = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: module.run()).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) unoptimized = { "mean": np.mean(unoptimized), "median": np.median(unoptimized), "std": np.std(unoptimized), } import tvm.auto_scheduler as auto_scheduler from tvm.autotvm.tuner import XGBTuner from tvm import autotvm number = 10 repeat = 1 min_repeat_ms = 0 # since we're tuning on a CPU, can be set to 0 timeout = 10 # in seconds # create a TVM runner runner = autotvm.LocalRunner( number=number, repeat=repeat, timeout=timeout, min_repeat_ms=min_repeat_ms, enable_cpu_cache_flush=True, ) tuning_option = { "tuner": "xgb", "trials": 20, "early_stopping": 100, "measure_option": autotvm.measure_option( builder=autotvm.LocalBuilder(build_func="default"), runner=runner ), "tuning_records": "resnet-50-v2-autotuning.json", } # begin by extracting the tasks from the onnx model tasks = autotvm.task.extract_from_program(mod["main"], target=target, params=params) print(tasks) # Tune the extracted tasks sequentially. for i, task in enumerate(tasks): prefix = "[Task %2d/%2d] " % (i + 1, len(tasks)) # choose tuner tuner = "xgb" # create tuner if tuner == "xgb": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="reg") elif tuner == "xgb_knob": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="reg", feature_type="knob") elif tuner == "xgb_itervar": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="reg", feature_type="itervar") elif tuner == "xgb_curve": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="reg", feature_type="curve") elif tuner == "xgb_rank": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_knob": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank", feature_type="knob") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_itervar": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank", feature_type="itervar") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_curve": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank", feature_type="curve") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_binary": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank-binary") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_binary_knob": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank-binary", feature_type="knob") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_binary_itervar": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank-binary", feature_type="itervar") elif tuner == "xgb_rank_binary_curve": tuner_obj = XGBTuner(task, loss_type="rank-binary", feature_type="curve") elif tuner == "ga": tuner_obj = GATuner(task, pop_size=50) elif tuner == "random": tuner_obj = RandomTuner(task) elif tuner == "gridsearch": tuner_obj = GridSearchTuner(task) else: raise ValueError("Invalid tuner: " + tuner) tuner_obj.tune( n_trial=min(tuning_option["trials"], len(task.config_space)), early_stopping=tuning_option["early_stopping"], measure_option=tuning_option["measure_option"], callbacks=[ autotvm.callback.progress_bar(tuning_option["trials"], prefix=prefix), autotvm.callback.log_to_file(tuning_option["tuning_records"]), ], ) with autotvm.apply_history_best(tuning_option["tuning_records"]): with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3, config={}): lib = relay.build(mod, target=target, params=params) dev = tvm.device(str(target), 0) module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev)) dtype = "float32" module.set_input(input_name, img_data) module.run() output_shape = (1, 1000) tvm_output = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(output_shape)).numpy() scores = softmax(tvm_output) scores = np.squeeze(scores) ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] for rank in ranks[0:5]: print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank])) import timeit timing_number = 10 timing_repeat = 10 optimized = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: module.run()).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) optimized = {"mean": np.mean(optimized), "median": np.median(optimized), "std": np.std(optimized)} print("optimized: %s" % (optimized)) print("unoptimized: %s" % (unoptimized)) ``` * Execute Result: ``` bash # No tune class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621103 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356379 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 [Task 1/25] Current/Best: 283.00/ 348.36 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 8.42 s Done. [Task 2/25] Current/Best: 74.32/ 278.44 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 5.78 s Done. [Task 3/25] Current/Best: 116.92/ 337.35 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.30 s Done. [Task 4/25] Current/Best: 304.23/ 328.07 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.33 s Done. [Task 5/25] Current/Best: 189.33/ 316.91 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.24 s Done. [Task 6/25] Current/Best: 221.74/ 314.72 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.33 s Done. [Task 7/25] Current/Best: 255.23/ 307.63 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.55 s Done. [Task 8/25] Current/Best: 26.67/ 299.85 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 8.58 s Done. [Task 9/25] Current/Best: 174.97/ 347.91 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 8.16 s Done. [Task 10/25] Current/Best: 154.63/ 280.17 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.48 s Done. [Task 11/25] Current/Best: 278.62/ 338.75 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.02 s Done. [Task 12/25] Current/Best: 224.97/ 308.45 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.64 s Done. [Task 13/25] Current/Best: 261.67/ 308.99 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.87 s Done. [Task 14/25] Current/Best: 92.82/ 312.59 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 12.86 s Done. [Task 15/25] Current/Best: 214.17/ 325.88 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.92 s Done. [Task 16/25] Current/Best: 207.14/ 267.99 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.40 s Done. [Task 17/25] Current/Best: 135.56/ 323.36 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.73 s Done. [Task 18/25] Current/Best: 199.88/ 292.03 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.68 s Done. [Task 19/25] Current/Best: 63.22/ 279.44 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.64 s Done. [Task 20/25] Current/Best: 16.96/ 287.96 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 12.55 s Done. [Task 21/25] Current/Best: 121.29/ 333.84 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 12.13 s Done. [Task 22/25] Current/Best: 258.80/ 267.89 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 6.79 s Done. [Task 23/25] Current/Best: 305.98/ 305.98 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 7.84 s Done. [Task 25/25] Current/Best: 0.00/ 0.00 GFLOPS | Progress: (0/20) | 0.00 s Done. [Task 25/25] Current/Best: 56.92/ 78.51 GFLOPS | Progress: (20/20) | 15.41 s Done. # Tune class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621104 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356378 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 TVM_CPU_Float32_Auto_Tune_XGB: {'mean': 0.03430713728850241, 'median': 0.033569534790149194, 'std': 0.004160319905261305} TVM_CPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.03740469979154296, 'median': 0.03763830485739163, 'std': 0.00046793406370928035} ``` #### 3.4.2. Float32 (GPU, gpu-Auto-tune) ``` python # just change target from llvm to cuda, use the code above target = "cuda" # or target = "cuda -arch=sm_89" # depends on your platform # use `nvcc --list-gpu-arch` to check ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash # No tune class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621104 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356378 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 # Tune class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621104 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356378 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019712 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 TVM_GPU_Float32_Auto_Tune_XGB: {'mean': 0.0067301002040039744, 'median': 0.006774019840086112, 'std': 0.00013180002687155013} TVM_GPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.0018996601785183885, 'median': 0.0019048284900782164, 'std': 1.3217539930054235e-05} ``` ### 3.4.3 Int8, cpu, tvm默认仅支持int8 ``` python import onnx from tvm.contrib.download import download_testdata from PIL import Image import numpy as np import tvm from tvm import relay from tvm.contrib import graph_executor from scipy.special import softmax import timeit onnx_model = onnx.load('resnet50-v2-7.onnx') img_path = 'kitten.jpg' resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224)) img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32") img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1)) imagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) norm_img_data = (img_data / 255 - imagenet_mean) / imagenet_stddev img_data = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0).astype("float32") input_name = "data" shape_dict = {input_name: img_data.shape} mod, params = relay.frontend.from_onnx(onnx_model, shape_dict) calibration_samples = [tvm.nd.array(img_data)] with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3): with relay.quantize.qconfig(calibrate_mode='global_scale', global_scale=8.0, skip_conv_layers=[]): quantized_mod = relay.quantize.quantize(mod, params, dataset=calibration_samples) target = "llvm" with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=3): lib = relay.build(quantized_mod, target=target, params=params) dev = tvm.device(str(target), 0) module = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev)) module.set_input(input_name, img_data) module.run() output_shape = (1, 1000) tvm_output = module.get_output(0, tvm.nd.empty(output_shape)).numpy() labels_path = "synset.txt" with open(labels_path, "r") as f: labels = [l.rstrip() for l in f] # Open the output and read the output tensor scores = softmax(tvm_output) scores = np.squeeze(scores) ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] for rank in ranks[0:5]: print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank])) timing_number = 200 timing_repeat = 10 unoptimized = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: module.run()).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) unoptimized = { "mean": np.mean(unoptimized), "median": np.median(unoptimized), "std": np.std(unoptimized), } print("TVM_CPU_Int8:", unoptimized) ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash One or more operators have not been tuned. Please tune your model for better performance. Use DEBUG logging level to see more details. class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.404191 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.210446 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.179177 class='n03223299 doormat, welcome mat' with probability=0.033031 class='n02127052 lynx, catamount' with probability=0.011398 TVM_CPU_Int8: {'mean': 0.12497943410099835, 'median': 0.1239671477425145, 'std': 0.004604382417633903} ``` #### 3.4.4. Int8 gpu tvm默认仅支持int8) ``` python target = 'cuda -arch=sm_89' ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash One or more operators have not been tuned. Please tune your model for better performance. Use DEBUG logging level to see more details. class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.404193 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.210444 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.179176 class='n03223299 doormat, welcome mat' with probability=0.033031 class='n02127052 lynx, catamount' with probability=0.011398 TVM_GPU_Int8: {'mean': 0.05043668361147866, 'median': 0.049358997289964464, 'std': 0.002297650553083921} ``` ### 3.5. TensorRT #### 3.5.1. Float32_GPU ``` python import tensorrt as trt import pycuda.driver as cuda import pycuda.autoinit import numpy as np import onnx import timeit from PIL import Image def check_result(output): from scipy.special import softmax labels_path = "synset.txt" with open(labels_path, "r") as f: labels = [l.rstrip() for l in f] scores = softmax(output) scores = np.squeeze(scores) ranks = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] for rank in ranks[0:5]: print("class='%s' with probability=%f" % (labels[rank], scores[rank])) onnx_file_path = 'resnet50-v2-7.onnx' # Got an warning omit it onnx_model = onnx.load(onnx_file_path) # Add trt logger TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING) runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) ## Avoid In node -1 (importModel): INVALID_VALUE: Assertion failed: !_importer_ctx.network()->hasImplicitBatchDimension() && "This version of the ONNX parser only supports TensorRT INetworkDefinitions with an explicit batch dimension. Please ensure the network was created using the EXPLICIT_BATCH NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag." Error explicit_batch = 1 << (int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH) with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_network(explicit_batch) as network, trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER) as parser: # parser the onnx model with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model: if not parser.parse(model.read()): for error in range(parser.num_errors): print("Error {}: {}".format(error, parser.get_error(error))) else: print("Model parsed successfully") # Check the network layers if need # for i in range(network.num_layers): # layer = network.get_layer(i) # print(layer.name, layer.get_output(0).shape) # config & build the trt engine, the warning can be omit config = builder.create_builder_config() config.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30 # 1GB engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) if engine is None: raise RuntimeError("Failed to create the TensorRT engine") # save the engine file if need (optinal), it contains the optimized result of the model graph engine_file_path = 'resnet50.trt' with open(engine_file_path, 'wb') as f: f.write(engine.serialize()) # load engine with open(engine_file_path, 'rb') as f: engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read()) # create context, context is like a handle context = engine.create_execution_context() img_path = 'kitten.jpg' # Resize it to 224x224 resized_image = Image.open(img_path).resize((224, 224)) img_data = np.asarray(resized_image).astype("float32") # Our input image is in HWC layout while ONNX expects CHW input, so convert the array img_data = np.transpose(img_data, (2, 0, 1)) # Normalize according to the ImageNet input specification imagenet_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) imagenet_stddev = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1)) norm_img_data = (img_data / 255 - imagenet_mean) / imagenet_stddev # Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW. host_input = np.expand_dims(norm_img_data, axis=0).astype("float32") # make sure the numpy is contiguous host_input = np.ascontiguousarray(host_input) # prepare input device_input = cuda.mem_alloc(host_input.nbytes) cuda.memcpy_htod(device_input, host_input) # prepare output output_shape = context.get_binding_shape(1) host_output = np.empty(output_shape, dtype=np.float32) device_output = cuda.mem_alloc(host_output.nbytes) # check the shape assert context.all_binding_shapes_specified assert context.get_binding_shape(0) == host_input.shape # execute context.execute_v2(bindings=[int(device_input), int(device_output)]) cuda.memcpy_dtoh(host_output, device_output) check_result(host_output) timing_number = 200 timing_repeat = 10 gpu_result = ( np.array(timeit.Timer(lambda: context.execute_v2(bindings=[int(device_input), int(device_output)])).repeat(repeat=timing_repeat, number=timing_number)) / timing_number ) gpu_result = {"mean": np.mean(gpu_result), "median": np.median(gpu_result), "std": np.std(gpu_result)} print("Tensorrt_GPU_Float32: %s" % (gpu_result)) ``` * Execution Result: ``` bash [05/22/2024-15:26:37] [TRT] [W] onnx2trt_utils.cpp:369: Your ONNX model has been generated with INT64 weights, while TensorRT does not natively support INT64. Attempting to cast down to INT32. Model parsed successfully test_tensorrt_resnet50_float32_gpu.py:50: DeprecationWarning: Use set_memory_pool_limit instead. config.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30 # 1GB test_tensorrt_resnet50_float32_gpu.py:51: DeprecationWarning: Use build_serialized_network instead. engine = builder.build_engine(network, config) [05/22/2024-15:26:38] [TRT] [W] TensorRT was linked against cuDNN 8.4.1 but loaded cuDNN 8.4.0 [05/22/2024-15:26:45] [TRT] [W] TensorRT was linked against cuDNN 8.4.1 but loaded cuDNN 8.4.0 [05/22/2024-15:26:45] [TRT] [W] The getMaxBatchSize() function should not be used with an engine built from a network created with NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH flag. This function will always return 1. [05/22/2024-15:26:45] [TRT] [W] The getMaxBatchSize() function should not be used with an engine built from a network created with NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH flag. This function will always return 1. [05/22/2024-15:26:45] [TRT] [W] TensorRT was linked against cuDNN 8.4.1 but loaded cuDNN 8.4.0 [05/22/2024-15:26:45] [TRT] [W] TensorRT was linked against cuDNN 8.4.1 but loaded cuDNN 8.4.0 class='n02123045 tabby, tabby cat' with probability=0.621154 class='n02123159 tiger cat' with probability=0.356326 class='n02124075 Egyptian cat' with probability=0.019713 class='n02129604 tiger, Panthera tigris' with probability=0.001215 class='n04040759 radiator' with probability=0.000262 Tensorrt_GPU_Float32: {'mean': 0.0011052313830005004, 'median': 0.0011054065149801316, 'std': 6.103668141089059e-07} ``` ### 3.6. Summary |Platform|Precision|Mean (s)|Median (s)|Std (s)| |-------|-------|-------|-----|--| |ONNXRuntime (CPU)|Float32|0.00998621|0.00998270|0.00001577| |ONNXRuntime (GPU)|Float32|0.00406905|0.00374741|0.00096074| |ONNXRuntime (CPU)|INT8|0.01137567|0.01137663|0.00001180| |ONNXRuntime (GPU)|INT8|0.01384249|0.01383995|0.00002146| |PyTorch (CPU)|Float32|0.02187023|0.02185894|0.00003488| |PyTorch (GPU)|Float32|0.00188753|0.00188261|0.00002818| |TVM (CPU, No tune)|Float32|0.03740470|0.03763830|0.00046793| |TVM (CPU, Auto-tune)|Float32|0.03430714|0.03356953|0.00416032| |TVM (GPU, No tune)|Float32|0.00189966|0.00190483|0.00001322| |TVM (GPU, Auto-tune)|Float32|0.00673010|0.00677402|0.00013180| |TVM (CPU)|INT8|0.12497943|0.12396715|0.00460438| |TVM (GPU)|INT8|0.05043668|0.04935900|0.00229765| |TensorRT (GPU)|Float32|0.00110523|0.00110541|0.00000061| 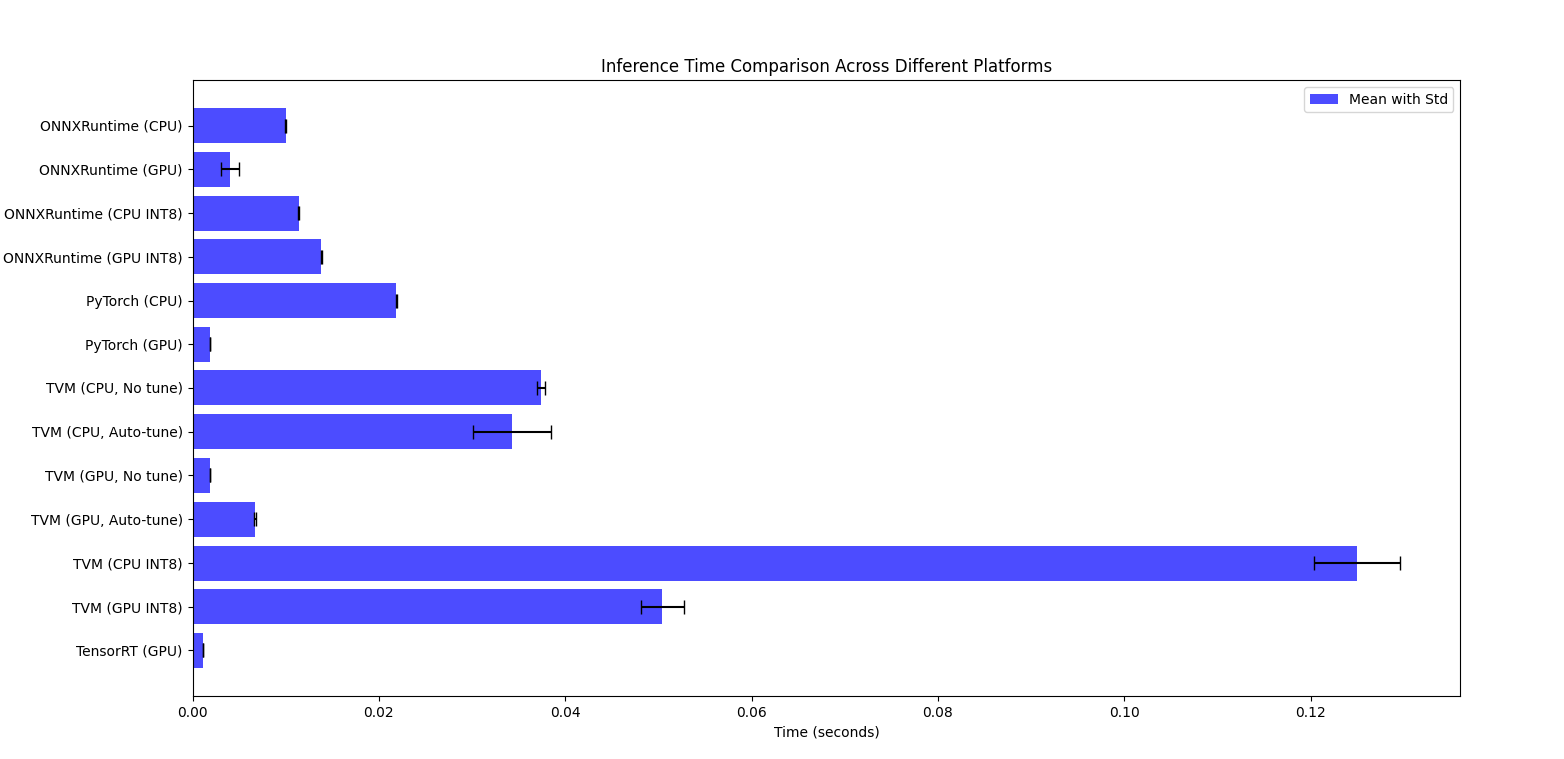
dingfeng
2024年5月28日 16:07
823
0 条评论
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
评论
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码