Public Docs
【模型量化】深度学习模型量化 & 量化理论 & 各平台的量化过程 & 硬件加速
【TVM】TI关于TVM的使用测试与分析
【LLM&LVM】大模型开源工程思维导图
SmartSip
【北航卓越工程师】《汽车前沿技术导论:智能驾驶》讲义
【工具链】Yocto使用介绍——使用Yocto创建一个树莓派的系统镜像
【工具链】使用ssh+dialog指令设定服务器指定用户仅容器访问
【推理引擎】一篇关于模型推理的详细对比与学习
【推理引擎】关于TVM中的Schedule优化详解(On going)
【LLM微调】使用litgpt进行私有数据集模型微调的测试总结
【TVM】在TVM Relay中创建一个自定义操作符
【STT+LLM+TTS】如何使用语音转文字模型+大预言模型+语音生成模型完成一个类人的语音交互机器人
【RAG】 通过RAG构建垂直领域的LLM Agent的方法探索
【RAG】GraphRAG精读与测试(On going)
【AI Agent】MetaGPT精读与学习
【AI Base】Ilya Sutskever 27篇必读论文分享清单
【Nvidia】Jetson AGX Orin/ Jetson Orin nano 硬件测试调试内容(On going)
【BI/DI】LLM Using in BI Testing Scenario (On going)
【Nvidia】How to Activate a Camera on Nvidia Platform in Details
【RAS-PI】树莓派驱动开发
【行业咨询阅读】关注实时咨询和分析
【mobileye】2024 Driving AI
【mobileye】SDS_Safety_Architecture
【yolo】yolov8测试
【nvidia】Triton server实践
【alibaba】MNN(on updating)
【OpenAI】Triton(on updating)
【CAIS】关于Compound AI Systems的思考
【Nvidia】关于Cuda+Cudnn+TensorRT推理环境
【BEV】BEVDet在各个平台上的执行效率及优化(On Updating)
【Chip】AI在芯片设计和电路设计中的应用
【Chip】ChiPFormer
【Chip】关于布线的学习
【Chip】MaskPlace论文精读与工程复现优化
【gynasium】强化学习初体验
【Cadence】X AI
【transformer】MinGPT开源工程学习
【中间件】针对apollo 10.0中关于cyberRT性能优化的深度解读和思考
【Robotics】调研了解当前机器人开发者套件(on updating)
【Robotics】ROS CON China 2024 文档技术整理与感想总结(上2024.12.7,中2024.12.8,下场外产品)
【algorithm】关于模型、数据与标注规范的平衡问题
【nvidia】DLA的学习了解与使用
【nvidia】构建nvidia嵌入式平台的交叉编译环境(其他环境平台可借鉴)
【2025AI生成式大会】2025大会个人总结
【Robotics】 Create Quadruped Robot RL FootStep Training Environment In IsaacLab
【Robotics】如何一个人较为完整的完成一个机器人系统软件算法层面的设计与开发
【VLM】读懂多模态大模型评价指标
【VLM】大模型部署的端侧部署性能与精度评估方法与分析
【Nvidia】Jetson Orin 平台VLM部署方法与指标评测
【Database】向量数据库
【SoC】性能与功耗评估
【MCP】MCP探索
文档发布于【Feng's Docs】
-
+
首页
【SoC】性能与功耗评估
# 0 Introduction 对一个SoC的执行功耗进行系统化分析也是SoC选型的一个重要依据,尤其是针对于产品化的评估和对功耗散热有严格要求的场景。所以在SoC选型前期如果能够根据实际情况对SoC的功耗进行系统化的评估判断,对于SoC的选型是一个非常重要的数据。本文将以Nvidia Jetson Orin(AGX/NX/Nano)为例对于如果系统性快速评测SoC的功耗进行分析。 # 1 了解配置 不同系列的SoC配置通常有所区别,除了本身的硬件区别外,类似像Jetson这样的平台还提供NvpModel(Nvidia Power Model)这样的软件模块,对于各个异构核的主频能够进行灵活的配置,从而在软件层面进行配置。也就是说即使你选择了Jetson AGX Orin,如果没有在nvpmodel层面对于相关异构核的主频进行配置,可能你的SoC也无法发挥出全部能力,自然无法充分评估功耗能力。 nvidia提供了一个 https://jetson-tools.nvidia.com/powerestimator/ 工具,可以用来通过一个web界面生成一个对应功耗的配置文件,在系统侧通过加载启用配置文件从而使得达到对应额定功耗的性能配置。 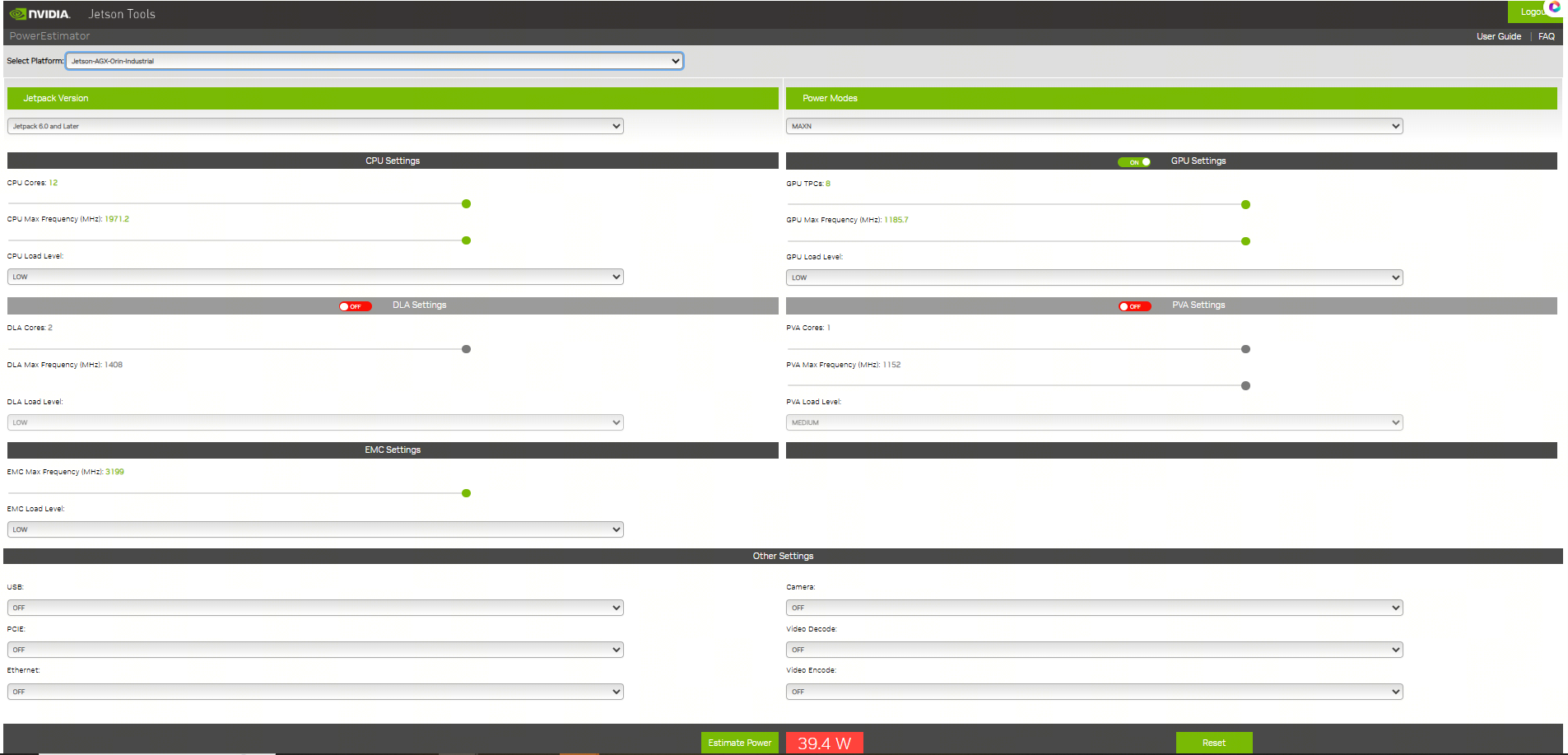 * 完成配置后,点击下载获得功耗对应的配置文件。 [【附件】nvpmodel (9).conf](/media/attachment/2025/12/nvpmodel_9.conf) * 端侧通过执行nvpmodel 指令加载和查看配置 ``` bash hihonor@tegra-ubuntu:~$ nvpmodel Nvidia Power Model Tool Version 1.1.4 Usage: nvpmodel [-h | --help] [--verbose] [-q | --query] [-p | --parse] [-u | --udata] [-w | --wait <sec>] [--boot] [--force] [-m | --mode <mode>] [-f | --conf <filename>] [-o | --os <android,l4t>] -h, --help: Print this help info. --verbose: Enable verbose log. --boot: Exit and do nothing if it is sanity-flashed build. --force: Automatically reboot if required when switching the power mode. -p, --parse: Parse the config file only. Recommended to enable verbose log. -m, --mode <mode>: <mode> is one of the integer POWER_MODEL ID defined in config file. Switch to the specified power mode. -f, --conf: explicitly specify the config file. If it is the only option, then it sets the power mode as default mode configured in the file. This option can be used for developer usage to specify a config file other than the default one. -o, --os <android,l4t>: Perform OS specific operations for power model settings. Argument is case insensitive. -q, --query: Query the current power mode. -w, --wait: delay execution by specified amount of seconds. -u, --udata: specify the absolute path for user data file when set or query power mode. Examples: nvpmodel -m 2: switch to POWER_MODEL ID=2 of which settings are defined in the default configuration file. nvpmodel -m 2 -o android: switch to POWER_MODEL ID=2 and perform Android specific operations for power mode. nvpmodel -m 2 -f pm.conf: switch to POWER_MODEL ID=2 of which settings are defined in pm.conf. nvpmodel -m 2 -u /data/status: switch to POWER_MODEL ID=2 and store the active mode as user settings in /data/status. nvpmodel -f pm.conf: read the active mode in user data file and set it as the power mode which is configured in pm.conf. If user data file does not exist or the active mode value is invalid, set defalut mode instead. nvpmodel -q: print the current power mode. nvpmodel -q --verbose: print the current power mode with verbose info. nvpmodel -p -f pm.conf: parse pm.conf and print the result. ``` # 2 功耗评测 功耗评测分成三个步骤:0. 完成配置,确认额定功耗;1. 负载生成;2. 负载查看;3. 功耗查看; ## 2.0 完成配置 根据需要或者要评测的额定功耗,完成对应配置,具体参见第1章节。 ## 2.1 负载生成 负载生成即对CPU,GPU,内存的资源添加对应的功耗。以linux系统为例: * stress-ng:一个Linux下的压力测试工具,可以对CPU、内存、I/O等进行负载,模拟不同的工作场景。 * CUDA样例程序:NVIDIA提供的CUDA示例程序可以用来生成GPU负载。 * 自定义深度学习推理任务:利用TensorRT或PyTorch等框架跑实际的推理任务,模拟真实负载。 ### 2.1.1 stress-ng #### 安装 1. 直接安装 ``` bash sudo apt install stress-ng ``` 2. 也可以使用源码安装 ``` bash git clone https://github.com/ColinIanKing/stress-ng.git cd stress-ng make sudo make install ``` #### 使用 * 使用4个CPU工作线程,运行60秒: `stress-ng --cpu 4 --timeout 60s` 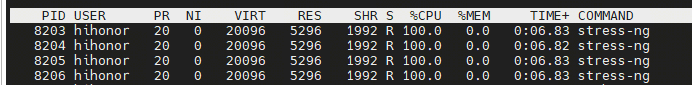 * 使用2个内存工作线程,分配并测试2GB内存,运行30秒:`stress-ng --vm 2 --vm-bytes 2G --timeout 30s` 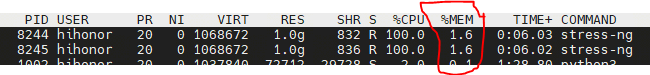 * 可以查看所有可添加负载:`stress-ng --help` ### 2.1.2 CUDA GPU 负载 需要使用 https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples nvidia提供的一些cuda-samples,如果是一些其他的SoC如npu或者tpu架构的SoC需要使用对应的工具去构建负载。 #### 安装 * 获取:`git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples.git` * 编译:`mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make` #### 使用 * 1. 查看当前型号 ``` bash hihonor@tegra-ubuntu:/data/cuda-samples/build/Samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery$ ./deviceQuery ./deviceQuery Starting... CUDA Device Query (Runtime API) version (CUDART static linking) Detected 1 CUDA Capable device(s) Device 0: "Orin" CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 12.2 / 12.2 CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 8.7 Total amount of global memory: 62842 MBytes (65894453248 bytes) (016) Multiprocessors, (128) CUDA Cores/MP: 2048 CUDA Cores GPU Max Clock rate: 1300 MHz (1.30 GHz) Memory Clock rate: 1300 Mhz Memory Bus Width: 256-bit L2 Cache Size: 4194304 bytes Maximum Texture Dimension Size (x,y,z) 1D=(131072), 2D=(131072, 65536), 3D=(16384, 16384, 16384) Maximum Layered 1D Texture Size, (num) layers 1D=(32768), 2048 layers Maximum Layered 2D Texture Size, (num) layers 2D=(32768, 32768), 2048 layers Total amount of constant memory: 65536 bytes Total amount of shared memory per block: 49152 bytes Total shared memory per multiprocessor: 167936 bytes Total number of registers available per block: 65536 Warp size: 32 Maximum number of threads per multiprocessor: 1536 Maximum number of threads per block: 1024 Max dimension size of a thread block (x,y,z): (1024, 1024, 64) Max dimension size of a grid size (x,y,z): (2147483647, 65535, 65535) Maximum memory pitch: 2147483647 bytes Texture alignment: 512 bytes Concurrent copy and kernel execution: Yes with 2 copy engine(s) Run time limit on kernels: No Integrated GPU sharing Host Memory: Yes Support host page-locked memory mapping: Yes Alignment requirement for Surfaces: Yes Device has ECC support: Disabled Device supports Unified Addressing (UVA): Yes Device supports Managed Memory: Yes Device supports Compute Preemption: Yes Supports Cooperative Kernel Launch: Yes Supports MultiDevice Co-op Kernel Launch: Yes Device PCI Domain ID / Bus ID / location ID: 0 / 0 / 0 Compute Mode: < Default (multiple host threads can use ::cudaSetDevice() with device simultaneously) > deviceQuery, CUDA Driver = CUDART, CUDA Driver Version = 12.2, CUDA Runtime Version = 12.2, NumDevs = 1 Result = PASS ``` * 2. 执行一些样例创建负载 因为不同平台的compute capability所有查遍编译时注意查看防止出现编译错误。例如nvidia jetson orin系列是compute_87 * 3. 也可以借助大模型评测 ``` mermaid flowchart TD A[自有数据集] -->|注册| B[LLM 性能评估<br/>Opencompass项目] A -->|注册| C[VLM 性能评估<br/>VLMEvalKit项目] D[EvalScope<br/>性能压测] -->|OpenaiAPI调用,评估TFTT、Throughput等| E[端侧部署<br/>docker容器化执行<br/>SGLang/vllM/transformer] B -->|OpenaiAPI调用,评估LLM能力| E C -->|OpenaiAPI调用,评估VLM能力| E F[模型] -->|部署/量化部署| E ``` 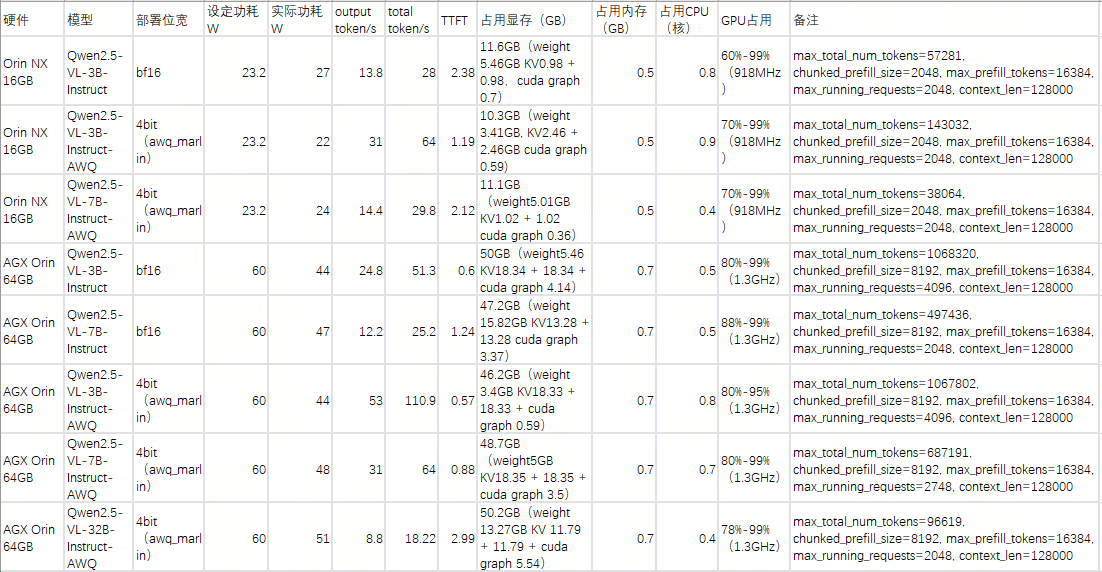 ## 2.2 负载查看 jtop,top,free,tegrastats这样的工具可以完整查看所有需要的负载指标 ## 2.3 功耗查看 借助示波器等硬件设备,查看实际功耗。 ## 2.4 标称参数 https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-jetpack-6-2-brings-super-mode-to-nvidia-jetson-orin-nano-and-jetson-orin-nx-modules/ 使用nvidia系列的设备,在配置不同功耗模式时还可以通过标称数据查看功耗模式是否匹配。例如jetson orin NX和Nano系列新推出的40W功耗super配置,在功耗提升配置时,其实只是dla和gpu的主频变化提升了运算能力。CPU在该模式下并没有出现变频或者提升的情况。所以在进行功耗配置时可以注意确认是否调整,以平衡需求。 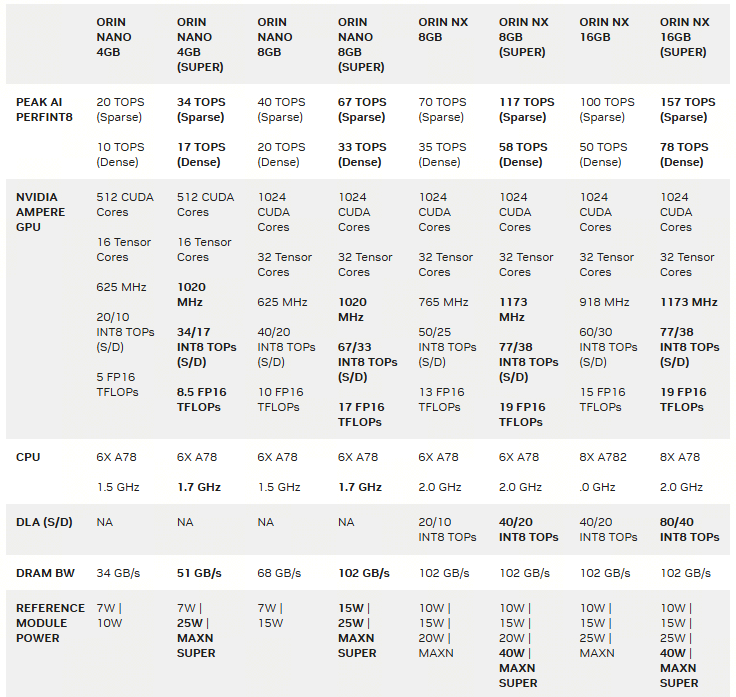 # 3 具体结果 ## 3.1 以Jetson AGX Orin的结果为例 ### 功耗设置和配置如下: ``` bash hihonor@tegra-ubuntu:~$ nvpmodel -q NV Power Mode: MODE_60_0_W 0 hihonor@tegra-ubuntu:~$ sudo tegrastats [sudo] password for hihonor: 12-09-2025 10:38:04 RAM 5443/62842MB (lfb 17x4MB) SWAP 0/31421MB (cached 0MB) CPU [100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201,100%@2201] EMC_FREQ 12%@2133 GR3D_FREQ 0%@[0,0] NVENC off NVDEC off NVJPG off NVJPG1 off VIC off OFA off NVDLA0 off NVDLA1 off PVA0_FREQ off APE 174 cpu@56.531C tboard@41.625C soc2@49.656C tdiode@43.125C soc0@50C tj@56.531C soc1@50.218C VDD_GPU_SOC 3047mW/3047mW VDD_CPU_CV 11809mW/11809mW VIN_SYS_5V0 6239mW/6239mW VDDQ_VDD2_1V8AO 2009mW/2009mW ``` ### CPU负载 | 满负载核心数 (n) | 平均功耗 (W)| cpu主频 (个数 x GHz) | | ---- | ---- | --- | |系统启动待机正常待机 0|9|0.73 x 12| |1|11|8 x 0.73 , 4 x 2.2| |2|13|12 x 2.2| |4|16|12 x 2.2| |6|18|12 x 2.2| |8|20|12 x 2.2| |10|23|12 x 2.2| |12|26|12 x 2.2| ### GPU负载 |GPU负载|平均试用功耗 (W)| |-|-| |持续负载80%-99%(1.3GHz)|45| |持续负载70%-99%(918MHz)|30|
dingfeng
2025年12月15日 14:28
192
0 条评论
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
评论
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码